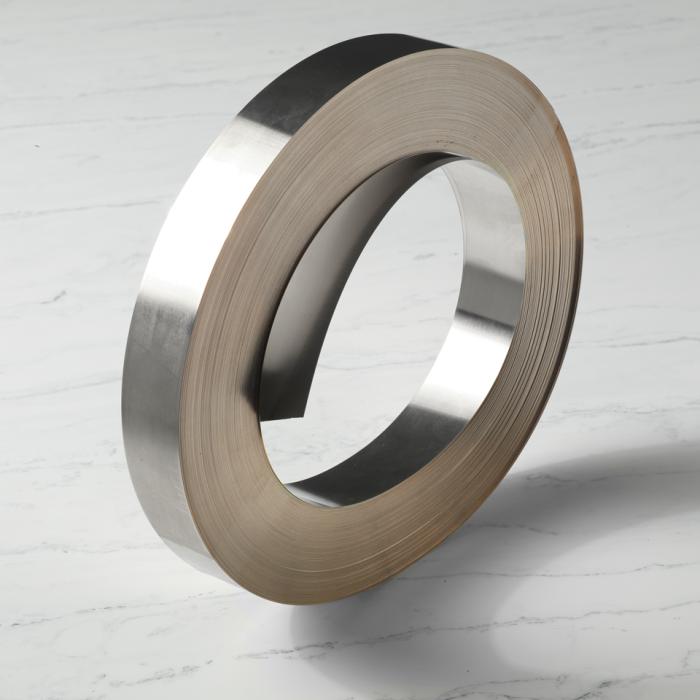
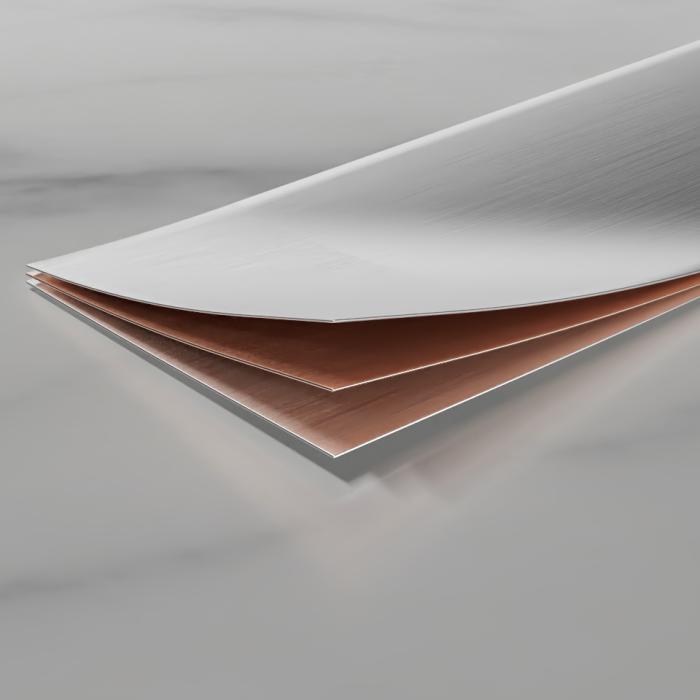
Trimetals
Trimetal alloys combine the tensile properties of copper with the versatility of silver alloys and are an effective and reliable choice for carbide-to-steel brazing, such as in toolmaking. A trimetal shim is a three-layer design with two outer strips of brazing filler metal clad onto a copper middle in a 1-2-1 ratio.
The copper core makes the trimetal unique among alloys. Copper withstands high temperatures, resists corrosion, and excellent for larger carbide applications that are prone to cracking or distortion due to differences in thermal expansion rates of base metals. The outer “jacket” consists of a combination of common filler metals such as:
- Silver (Ag), the standard for non-ferrous and ferrous applications, provides versatility, high strength and low melting points
- Nickel (Ni) and Manganese (Mn) aid carbide wetting, corrosion protection, and strengthen the bond
- Cadmium* (Cd) affords higher mechanical strength and a harder, more wear-resistant joint; it can also be used at lower working temperatures
- Zinc (Zn) is used for its corrosion protection
Resources Center
We work closely with our customers to provide guidance and support on brazing and medical precious metal related issues.